To decipher hearing disorders
We aim at understanding signaling pathways underlying the degeneration of cochlear neuro-epithelium in acquired (e.g. noise-, ototoxic drug-induced), age-related and genetic hearing loss using disease-specific model systems, as well as endangered species such as marine mammals.
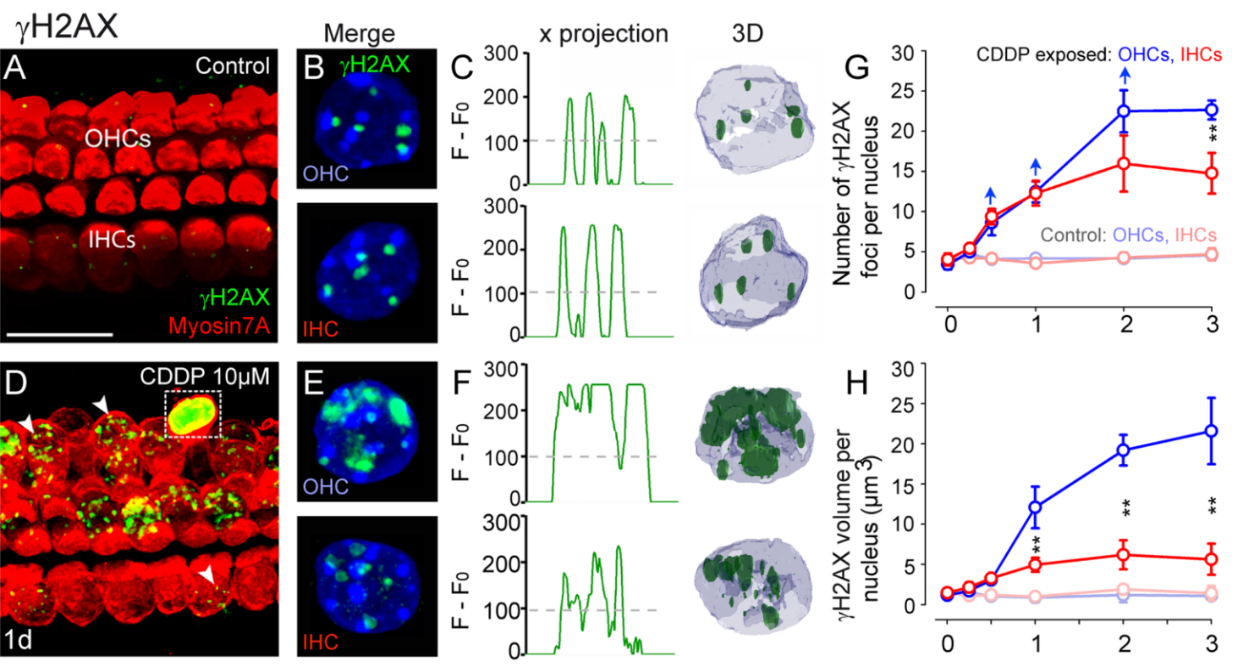
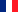
Mechanisms of cisplatin ototoxicity. Cochlea explants poisoning with cisplatin leads to DNA damage in the nuclei of the outer hair cells. Activation of the ATM‐Chk2‐p53 pathway is the major determinant of cisplatin ototoxicity. Systemic administration of a p53 inhibitor in mice bearing patient‐derived triple‐negative breast cancer protected auditory function, without compromising the anti‐tumor efficacy of cisplatin. (Benkafarda et al. EMBO Mol Med. 2017)
Towards hearing rescue
Our final goal is to restore hearing. Our studies have demonstrated that administration of pharmacological compounds can prevent sensory hair-cell death and restore auditory function in animal models of noise-induced hearing loss. These results lead to clinical trials, which are under development with pharmaceutical companies. Using viral gene transfer, we aim to restore hearing through replacement of defective genes and to regenerate the hair cells in mouse models of human genetic and acquired deafness.
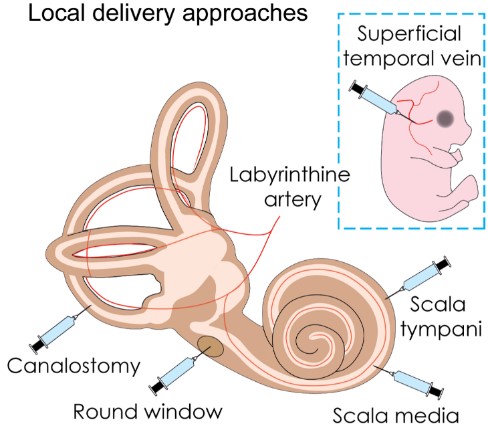
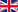
Route of administration. Shown are established routes for gene delivery into the perilymph via a cochleostomy or trans-round-window membrane route; into the endolymph via cochleostomy of the scala media space, and canalostomy. Insert: shown is the systemic delivery of AAV9 via the superficial temporal vein. (Wang and Puel, Physiological Review 2018).
Major publications
Benkafadar N et al., Molecular Neurodegeneration, in press
Wang J and Puel JL, Physiol Rev. 98(4):2477-2522, 2018
Benkafadar N et al., EMBO Mol Med. 9(1):7-26, 2017
Morell M et al., J Comp Neurol. 15;523(3):431-48, 2015
Bourien J et al., J Neurophysiol. 112(5):1025-39, 2014
Patents
WO2017125429 A1: The use of a temporary inhibitor of p53 for preventing or reducing cancer relapse.
WO 2007119098 A3: Methods for the treatment of tinnitus induced by cochlear excitotoxicity.
WO 2005092345 A1: Use of a phenothiazine derivative for preventing and/or treating hearing loss.
Collaborations
- Salah El-Mestikawy, McGill University, Canada
- Isabel Varela-Nieto, Institute for Biomedical Research, Spain
- Guy Lenears, Angers University, Angers, France
- Alexis Bemelmans, Institut de biologie François Jacob, Paris, France
- François Casas, University Montpellier, France
Fundings